No products in the cart.
Other Info
R134a refrigerant replacement
R-134a refrigerant has been widely used in automotive air conditioning systems, commercial refrigeration, and other applications. However, due to its high Global Warming Potential (GWP), there is a global push to phase out R-134a and replace it with more environmentally friendly alternatives. Below are some common replacements for R-134a: R134a Refrigerant replacement.
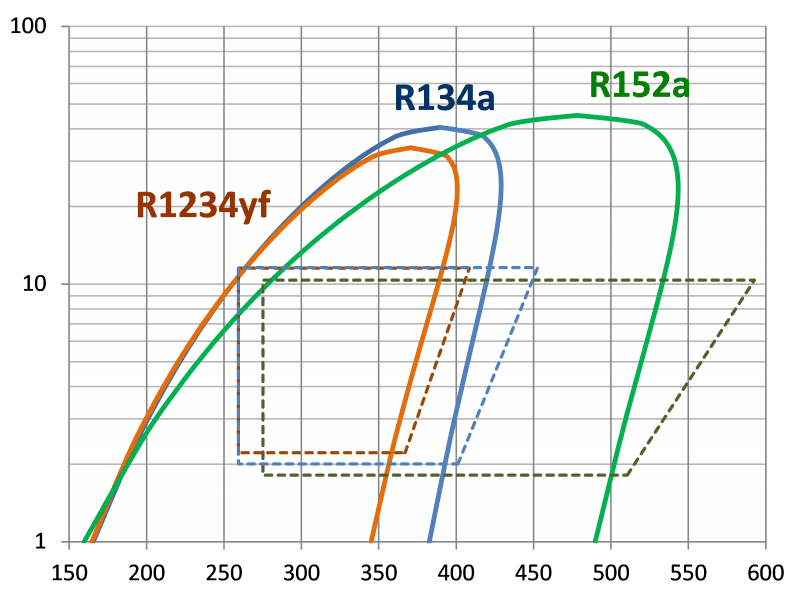
1. R-1234yf
- Properties: R-1234yf is a hydrofluoroolefin (HFO) refrigerant with a significantly lower GWP (GWP = 4) compared to R-134a (GWP = 1430).
- Applications: Primarily used in automotive air conditioning systems as a drop-in or near-drop-in replacement for R-134a.
- Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly (low GWP).
- Compatible with existing R-134a systems with minor modifications.
- Disadvantages:
- Flammable (classified as A2L, mildly flammable).
- Higher cost compared to R-134a.
2. R-513A
- Properties: R-513A is a blend of R-1234yf and R-134a, with a GWP of 573.
- Applications: Used in commercial refrigeration and chillers as a replacement for R-134a.
- Advantages:
- Lower GWP than R-134a.
- Non-flammable (classified as A1).
- Good performance in existing systems with minimal retrofitting.
- Disadvantages:
- Slightly higher GWP than R-1234yf.
3. R-450A
- Properties: R-450A is a blend of R-1234ze and R-134a, with a GWP of 547.
- Applications: Suitable for commercial refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- Advantages:
- Lower GWP than R-134a.
- Non-flammable (classified as A1).
- Disadvantages:
- Requires system adjustments for optimal performance.
4. R-744 (CO₂)
- Properties: R-744 is carbon dioxide, a natural refrigerant with a GWP of 1.
- Applications: Used in commercial refrigeration, heat pumps, and some automotive air conditioning systems.
- Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly (very low GWP).
- Non-flammable and non-toxic.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires high-pressure systems, which can be costly to implement.
- Less efficient in high ambient temperatures.
5. Hydrocarbon Refrigerants (e.g., R-290 (Propane))
- Properties: Hydrocarbon refrigerants like R-290 have very low GWP (GWP = 3) and are highly efficient.
- Applications: Used in small refrigeration systems and some air conditioning applications.
- Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly (very low GWP).
- High energy efficiency.
- Disadvantages:
- Highly flammable (classified as A3).
- Limited to smaller charge systems due to safety concerns.
Top replacement for R-134a
6. R-152a
- Properties: R-152a is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) with a GWP of 138.
- Applications: Used in some automotive and commercial refrigeration systems.
- Advantages:
- Lower GWP than R-134a.
- Good thermodynamic properties.
- Disadvantages:
- Flammable (classified as A2).
Considerations When Replacing R-134a
- System Compatibility: Ensure the replacement refrigerant is compatible with the existing system components (e.g., compressor, seals, lubricants).
- Regulatory Compliance: Check local and international regulations (e.g., F-Gas Regulation in the EU, EPA regulations in the US).
- Safety: Consider flammability and toxicity of the replacement refrigerant.
- Performance: Evaluate the thermodynamic properties and efficiency of the replacement refrigerant.
- Cost: Factor in the cost of retrofitting or replacing equipment.
Phasing Out R-134a
Many countries are phasing out R-134a due to its high GWP. For example:
- The European Union’s F-Gas Regulation restricts the use of high-GWP refrigerants like R-134a.
- The US EPA has listed R-134a as unacceptable in certain applications under the SNAP (Significant New Alternatives Policy) program.
If you’re considering replacing R-134a, consult with a refrigeration or HVAC professional to determine the best alternative for your specific application. R-134a Refrigerant replacement check our product page.


